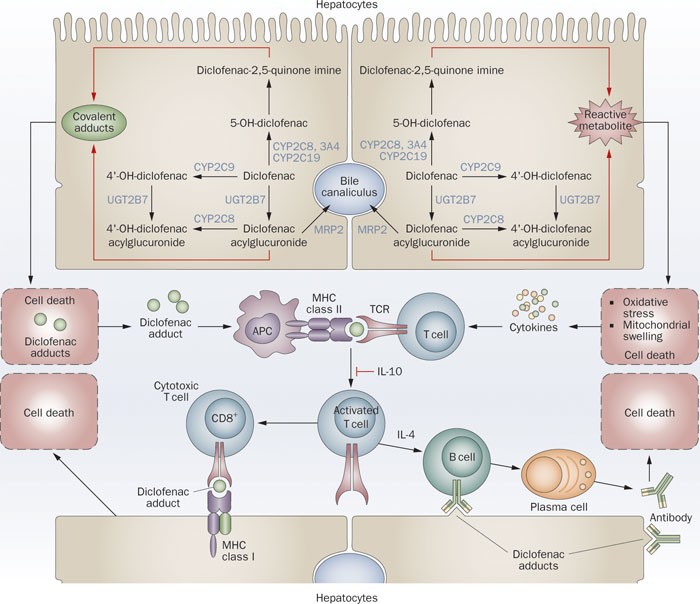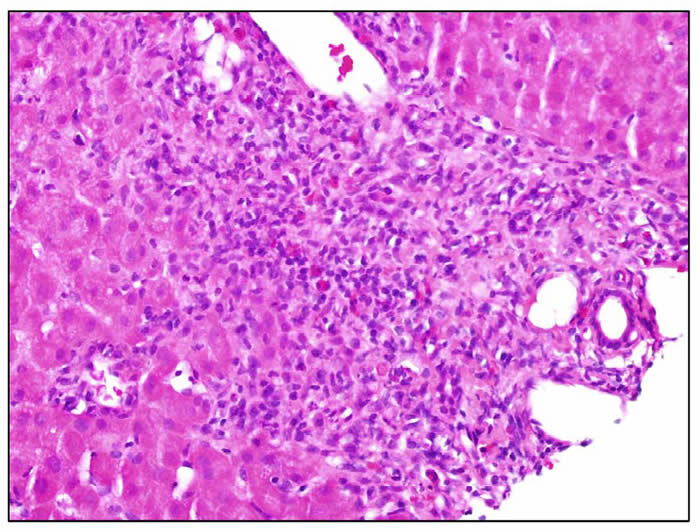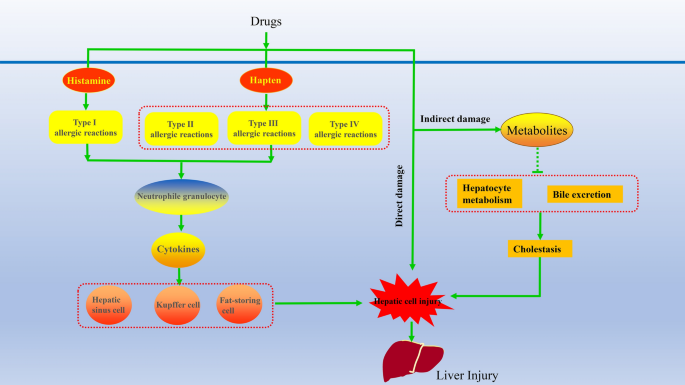
Mechanism of drug-induced liver injury and hepatoprotective effects of natural drugs | Chinese Medicine | Full Text
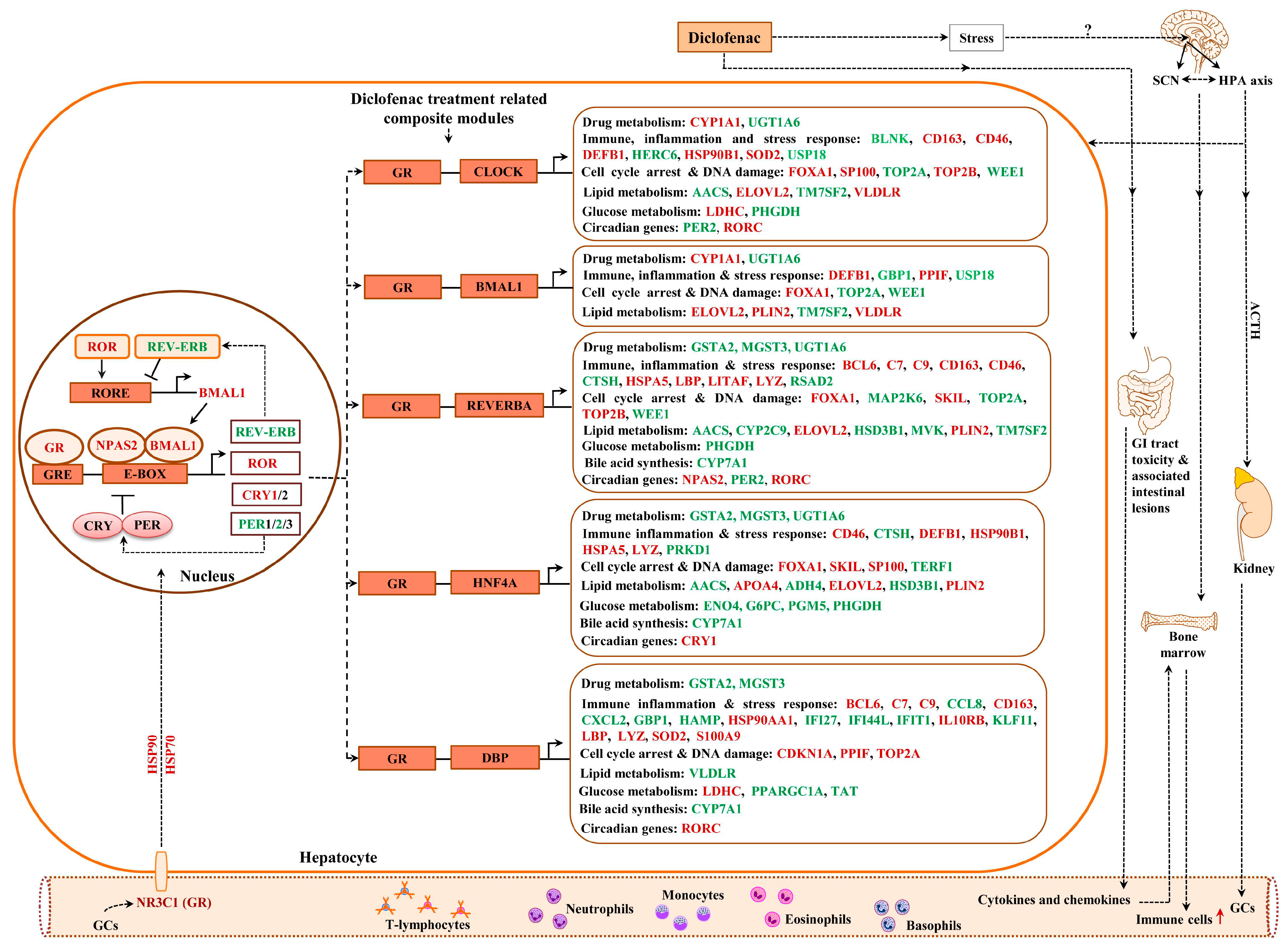
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Diclofenac Disrupts the Circadian Clock and through Complex Cross-Talks Aggravates Immune-Mediated Liver Injury—A Repeated Dose Study in Minipigs for 28 Days
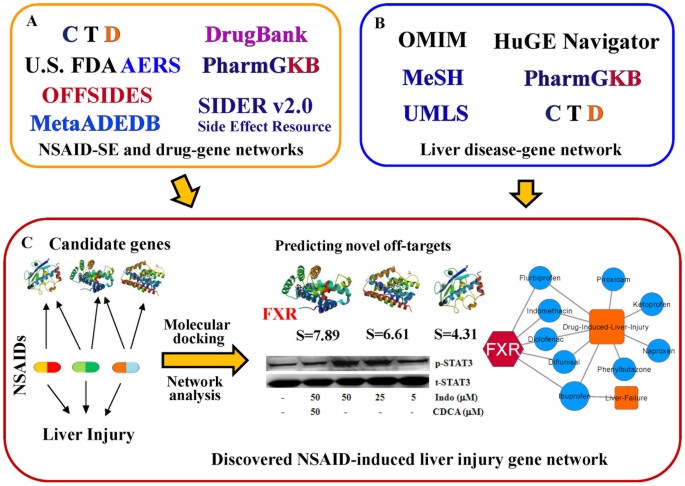
FXR antagonism of NSAIDs contributes to drug-induced liver injury identified by systems pharmacology approach | Scientific Reports

Evaluation of the Potential for Drug-Induced Liver Injury Based on in Vitro Covalent Binding to Human Liver Proteins | Drug Metabolism & Disposition

Biocomponents from Opuntia robusta and Opuntia streptacantha fruits protect against diclofenac-induced acute liver damage in vivo and in vitro - ScienceDirect

Genetic Susceptibility to Diclofenac-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Contribution of UGT2B7, CYP2C8, and ABCC2 Genotypes - ScienceDirect

Protection from diclofenac-induced liver injury by Yulangsan polysaccharide in a mouse model - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanism of drug-induced hepatotoxicity: current understanding and future perspectives | Semantic Scholar PDF] Mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanism of drug-induced hepatotoxicity: current understanding and future perspectives | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/eb53ad73fcd63220142cb170bff89ad0f719d198/41-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanism of drug-induced hepatotoxicity: current understanding and future perspectives | Semantic Scholar
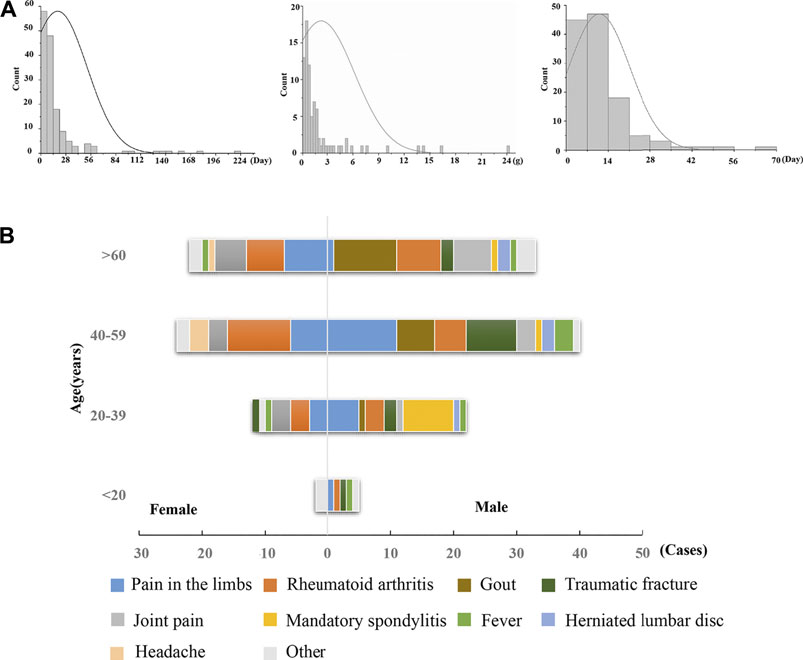
Frontiers | Screening for Susceptibility-Related Biomarkers of Diclofenac-Induced Liver Injury in Rats Using Metabolomics

The effect of LPS and heparin on diclofenac-induced liver injury. Rats... | Download Scientific Diagram

Development of Novel Diclofenac Analogs Designed to Avoid Metabolic Activation and Hepatocyte Toxicity | ACS Omega

Cancers | Free Full-Text | Development and Challenges of Diclofenac-Based Novel Therapeutics: Targeting Cancer and Complex Diseases








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Voltaren-Diclofenac-vs-Advil-Ibuprofen_Illustrator_Julie-Bang_Final-55f7a010bb6a400288fa4abf8dd71f50.jpg)